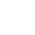
Product Name: Lanthanum Carbide (LaC2)
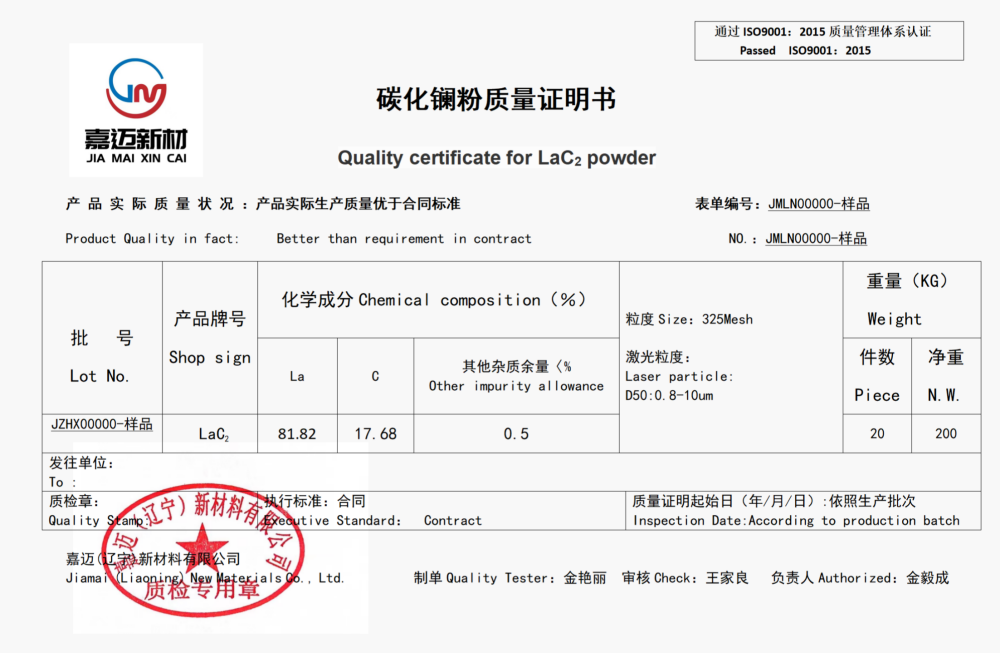
Specification: 0.8-10um (D50)
Appearance: Irregular
Color: Black Grey
Features: high melting point of about 2360 ° C; high density of about 5.29 g/cm ³; The high conductivity resistivity is about 68.0 μ Ω· cm
Usage: Used in scenarios that require extreme high temperature tolerance, such as aerospace engine components or core materials for high-temperature furnaces. Based on the catalytic and optical properties of lanthanum element, it has applications in special catalysts, functional ceramic additives, and other fields



LANTHANUM CARBIDE
CAS number: 12071-15-7
Molecular formula:LaC2
Molecular weight: 162.93
Melting point: 2360 ° C
Density: 5.290
Accurate molecular weight: 162.90600
Production process:
- High temperature solid-state reaction method: Mix metal lanthanum with graphite powder in proportion, with graphite usually in excess of 5% to 10%. The mixture is placed in a Pyrex reaction tube and gradually heated to 1700 ℃ by induction heating under inert atmosphere (such as argon or helium) protection, and kept at that temperature for about 30 minutes. Then, it is naturally cooled to obtain lanthanum carbide product. This method needs to be operated in a glove box to ensure complete isolation from air and moisture.
- Arc melting method: Weigh high-purity lanthanum metal and carbon powder in a stoichiometric ratio, mix and press them into blocks in a vacuum glove box (pressure of about 25-40 tf/in). The pressed block is then placed in an arc melting furnace and subjected to arc melting in a high-purity helium or argon atmosphere, allowing the metal to fully react with carbon to produce lanthanum carbide. This method is suitable for preparing high-purity and dense lanthanum carbide materials.
- Hydrogen intermediate gas method: First, react metal lanthanum with hydrogen gas to generate lanthanum hydride (LaH3), and then mix lanthanum hydride with graphite powder uniformly under argon protection. The mixture is heated to 1200 ℃ in a vacuum furnace and kept at that temperature for 30 minutes, allowing lanthanum hydride to react with carbon to form lanthanum carbide (La ₂ C3). This method is commonly used to prepare lanthanum carbide tungsten composite hot cathode materials, which can reduce reaction temperature and improve product uniformity.
Application fields:
- Ultra high temperature structures/refractory materials (essential for military, aerospace, and metallurgical industries)
-Core advantages: high melting point+high hardness+metal conductivity+rare earth reinforcement
-High temperature alloy/ceramic matrix composites (CMCs) reinforcement phase, used for missile nozzles, rocket throat liners, and hypersonic structures
-Metallurgical crucible, heating element, high-temperature mold, wear-resistant parts
-Aircraft engine/gas turbine hot end coating, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant coating
- Superconductivity and Quantum Materials (Frontier Electronics, Quantum Computing)
-As a rare earth carbon based superconducting precursor/doping phase, used for preparing low/high temperature superconducting thin films and bulk materials
-Carbon nanotube/graphene doping modification enhances conductivity, thermal conductivity, and structural strength, making it suitable for high-frequency devices, quantum chips, and superconducting magnets
- Military special materials (ammunition, armor, guidance)
-Hard alloy/armor piercing core reinforced with rare earth carbides to enhance density, hardness, and penetration depth
-Armor steel/ceramic armor second phase, toughening, anti fragmentation, impact resistance
-Infrared/electro-optical window, radar cover ceramic substrate, suitable for guidance, night vision, electronic warfare
- Nuclear industry and radiation environment
-Neutron absorption/slowing characteristics adaptation, can be used as candidate materials for nuclear reactor structures, cladding, and reflector layers
-Radiation resistant, high-temperature stable, used for lining and controlling materials in fusion/fission reactors
- Electronics and Coating (Semiconductor, Optoelectronics)
-High purity LaC ₂ sputtering target material, used for coating superconducting thin films, photodetectors, and microwave devices
-Rare earth carbide conductive ceramics, suitable for high-temperature electrodes, sensors, and corrosion-resistant electronic components
- Chemical and metallurgical additives
-High purity carbon and lanthanum sources for microalloying of special steels, high-temperature alloys, and rare earth permanent magnets
-Acetylene generator, organic synthetic carbon source
Packaging and storage: This product is packaged in an inert gas filled plastic bag, sealed and stored in a dry and cool environment. It should not be exposed to air to prevent moisture from causing oxidation and aggregation, which may affect dispersion performance and usage effectiveness; The packaging quantity can be provided according to customer requirements and divided into smaller packages.